Arch Linux
Arch Linux is the preferred distro and the only one that is currently supported.
Since it can be complicated to install arch, we also suggest trying CachyOS since it has a very easy step by step guide, and it has an amazing out-of-the-box experience. Aswell as that, it also has the kernel modifications we do for linux-g14 base into the cachyos kernel. So, you can skip the kernel installation.
CachyOS and manjaro have the asus g14 kernel patchset already included and you can skip installing the custom kernel: everything is ready OOTB!
Other (less newcomers-friendly) notable arch-derivate distros are: EndeavourOS and garuda.
If you own a ROG Ally or ROG Ally X ChimeraOS might be a good choice.
Intro
Read the Intro guide first to avoid bad surprises.
Installation
To install Arch just follow the regular installation guide for the official archlinux or the procedure provided by your distro of choice.
The suggested bootloader is systemd-boot. Avoid using GRUB.
Also remember to install these:
pacman -S linux-firmware amd-ucode intel-ucode
choose either amd-ucode or intel-ucode depending on your CPU.
If you are using the official archlinux read the article about vulkan and install whatever your iGPU might need.
Repo
g14 repo contains all the tools you need on a ROG laptop precompiled for you. g14 is only a name and all tools from it apply to most ROG laptops Before adding the repo you need to add the repo sign key to your pacman-key. Run the following commands to add it:
pacman-key --recv-keys 8F654886F17D497FEFE3DB448B15A6B0E9A3FA35
pacman-key --finger 8F654886F17D497FEFE3DB448B15A6B0E9A3FA35
pacman-key --lsign-key 8F654886F17D497FEFE3DB448B15A6B0E9A3FA35
pacman-key --finger 8F654886F17D497FEFE3DB448B15A6B0E9A3FA35
This should show output similar to this:
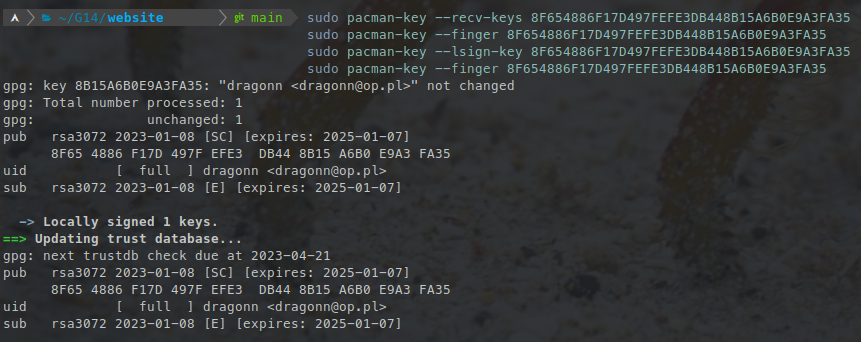 If you have any problems check if
If you have any problems check if /etc/pacman.d/gnupg/gpg.conf doesn't have specified the keyserver or make sure it is hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com
If you still have problems check if you are not running some active VPN connection, this does sometimes cause problems when fetching the server.
If you still have problems you can do it the less proper way by running those commands:
wget "https://keyserver.ubuntu.com/pks/lookup?op=get&search=0x8b15a6b0e9a3fa35" -O g14.sec
sudo pacman-key -a g14.sec
After that to get the repo add to your /etc/pacman.conf at the end:
[g14]
Server = https://arch.asus-linux.org
You could use a mirror instead if the origin has slow connection. Following is a list of available servers:
https://arch.asus-linux.org # Germany, origin
https://naru.jhyub.dev/$repo # Republic of Korea
After adding the repo run a full system update before you go to install tools from the repo:
pacman -Suy
Asusctl - custom fan profiles, anime, led control etc.
The recommended way to install asusctl is using g14 pacman repo. Packages like asusctl-git from AUR aren't supported. Also installing manually from cloned git isn't supported. For installing it run:
pacman -S asusctl power-profiles-daemon
asusd service is triggered by a udev rule after the keyboard driver is ready, the service doesn't need to be enabled and is not supposed to be.
power-profiles-daemon is optional but highly recommend, other power management tools can create conflicts with asusctl or supergfxctl.
systemctl enable --now power-profiles-daemon.service
Be aware that some functions or asusctl need kernel level drivers support, take a look at the "Custom kernel section"
Supergfxctl - graphics switching
WARNING supergfxctl is being phased out and its use is unadvised. During this transitioning period where an alternative is unavailable, unless you require vfio for virtual machines or have problems turning off your dGPU don't install it!
WARNING Read the supergfxctl manual first!
The same rules as for asusctl, installing:
pacman -S supergfxctl
Enable and start the systemd service:
systemctl enable --now supergfxd
supergfxctl can be used without asusctl.
ROG Control Center
ROG Control Center is a GUI tool for configuring few aspects of asusctl and supergfxctl. It was previously part of the asusctl package, but has now been separated as its own package in G14 repo. After adding the repo to /etc/pacman.conf as stated above, then you can install the tool:
pacman -S rog-control-center
Custom kernel - drivers fixes, hardware support
Newer devices often require custom kernel with patches, that kernel is also available in the g14 pacman repo, to install it just run:
pacman -Sy linux-g14 linux-g14-headers
Again, don't get confused by the name, it exists only for historical reasons.
If you are using a custom kernel use the nvidia-open-dkms package for nvidia drivers, the regular nvidia package works only with stock Arch kernel
At the date of updating this article devices from 2023 and older shouldn't need a custom kernel, fixes for 2024 are currently be worked on.
Be aware that this state might change more often then this guide gets updated.
After installing the new kernel you need to regenerate your boot menu or add a new boot entry depending on what boot manager you are using. For GRUB that will be:
grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg
For others refer to their documentation/Arch Wiki page. You can check currently booted kernel with command uname -r. It should give you for example:
6.8.1-arch1-g14-1
The -g14 part is the important one.
nVidia
Turing architecture (GTX 1000 cards)
Systems equipped with a Turing architecture GPU (for example, GTX 1650 in the Zephyrus G14, GA401IHR) require manual installation of the udev rules and modprobe configuration provided by nvidia-laptop-power-cfg with some slight modifications.
- Install the proprietary NVIDIA driver package. According to the Arch Wiki, Turing GPUs cannot enable proper power management when GSP firmware is active. You cannot disable GSP firmware on nvidia-open package. The proprietary driver package must therefore be used to enable correct power management functionality.
- Create the modprobe configuration.
Create
/etc/modprobe.d/nvidia.confwith the following contents:
options nvidia_drm modeset=1
options nvidia NVreg_EnableGpuFirmware=0 NVreg_EnableS0ixPowerManagement=1 NVreg_DynamicPowerManagement=0x02
NVreg_EnableGpuFirmware=0 is necessary here to disable GSP firmware.
- Add the udev rule.
Create
/usr/lib/udev/rules.d/80-nvidia-pm.ruleswith the contents from: https://gitlab.com/asus-linux/nvidia-laptop-power-cfg/-/blob/main/nvidia.rules
Ampere architecture (RTX 2000) or later
If you have an nvidia GPU with Ampere architecture or later on your laptop You should install nvidia-laptop-power-cfg
git clone https://gitlab.com/asus-linux/nvidia-laptop-power-cfg.git
cd nvidia-laptop-power-cfg
makepkg -sfi
Next steps
If you haven't done already enable nvidia services:
systemctl enable nvidia-suspend.service nvidia-hibernate.service nvidia-resume.service
systemctl enable --now nvidia-powerd
# Only enable this if you plan to use the feature (unless you know exactly what it does don't touch it)
# systemctl enable nvidia-suspend-then-hibernate.service
After a reboot you should see the GPU turning on when needed and off when it's not needed anymore.
Additionally you should query the status of your GPU with
cat /proc/driver/nvidia/gpus/bus_address/power
the bus_address will be different on each model, just use the autocompletion feature of bash spamming tab; the correct result is similar to this:
S0ix Power Management:
Platform Support: Supported
Status: Enabled
If S0ix platform support is supported you want to ensure it is enabled: this is important for sleep and idle power consumption!
Make sure you also install the vulkan adapter for mesa as well:
pacman -S nvidia-utils vulkan-icd-loader
NOTE For this supergfxctl is NOT needed!
When the laptop is fully configured you should see the rog-control-center icon in the taskbar (if you have a taskbar like in KDE) that changes between blue and red color depending on the nvidia status. A quick test is ensuring it is blue when no external screen or USB-C dock is connected and it goes red when you execute the command:
nvidia-smi
Secure Boot
Arch
On arch NOT FOR DERIVATES you can use the AUR package sbctl-dracut-conf to quickly configure the system for secure boot.
Install that package, put your laptop in Setup Mode on the UEFI menu and boot into archlinux, then issue:
sbctl create-keys
sbctl enroll-keys -m
dracut-regen
Then it is best to reinstall the kernel and ensure it got signed.
You have to ensure the bootloader is signed too, otherwise the UEFI won't load it and display you an error message about insecure OS being prevented to be loaded.
To check signed files you have to use
sbctl list-files
A correctly configured system produces this output:
sudo sbctl list-files
/efi/EFI/refind/refind_x64.efi
Signed: ✓ Signed
Output File: /efi/EFI/BOOT/BOOTX64.EFI
/efi/EFI/Linux/linux-g14.efi
Signed: ✓ Signed
In this case you can see my UEFI loading /efi/EFI/BOOT/BOOTX64.EFI on boot, so I sign /efi/EFI/refind/refind_x64.efi and put the result into the file that gets loaded at boot.
The other file is the kernel initramfs that is loaded by the bootloader: I sign it in-place.
After the first reboot your laptop will automatically exit setup mode and secure boot will work.
If you don't have the bootloader listed in that table run
sbctl sign -s -o "/efi/EFI/BOOT/BOOTX64.EFI" "/efi/EFI/<file>"
where file might be either the .efi file under refind, systemd-boot, grub or whatever else bootloader you might be using.
If you don't see the kernel appearing in the table of signed files reinstall the kernel: this will trigger the automatic signing process.
This is a do-and-forget thing: once the initial setup is done no manual intervention is needed and every new kernel will be automatically signed.
WARNING do not attempt this on anything else than arch: cachyos will surely be rendered unbootable and other distros are untested.
CachyOS
To enable Secure Boot on CachyOS, please follow the CachyOS Secure Boot Setup guide.
Other distros based on Arch
EndeavourOS
When installing EndeavourOS do not use the option with the Nvidia drivers preinstalled. This installs configs which might conflict with supergfxctl, furthermore that driver only works with the stock kernel. Use the default install option then install nvidia-open-dkms post install.
